On this page
Overview
This tutorial enables any developer or an architect to quickly deploy the Curity Identity Server to the AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service.
This installation follows the security best practice to host the Curity Identity server and the APIs behind an Ingress controller acting as an reverse proxy/API gateway. This will ensure that opaque access tokens are issued to internet clients, while APIs receive JWT access tokens. This design is called the Phantom Token Approach.
This tutorial could be completed mostly by using the AWS Cloud Platform free tier option but the EKS control plane might incur some costs.
Components and URLs
NGINX Ingress Controller
Following components are deployed in the k8s cluster by running ./deploy-idsvr-aws-eks.sh --install
| Component | Base URL | namespace | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curity Admin | https://admin.example.eks | curity | The URL for the Identity Server admin console |
| Curity Runtime | https://login.example.eks | curity | The URL for runtime nodes of the Identity Server |
| Example API | https://api.example.eks/echo | api | API endpoint protected by the phantom-token flow |
| Phantom Token Plugin | NA | NA | Plugin for transforming opaque tokens in to by value JWT tokens |
| NGINX Ingress controller | NA | ingress-nginx | NGINX Ingress controller for routing requests to different services in the k8s cluster, also acts as the gateway in front of the APIs and transforms opaque access tokens to JWTs |
Curity Admin URL is typically not exposed to the internet and kept internal but since this is a demo installation for evaluation and study purposes, the admin url has been exposed.
URLs
This tutorial will alias the load balancer public IP address to local development domain names, which provides an easy and free way for developers to use real world URLs. However in an enterprise setup, you would create globally resolvable custom internet domain names using a paid domain name service like AWS Route 53.
Installation
The deployment process is automated via a simple bash script. The deployment script asks to provide an option to either use eksctl or terraform to manage the AWS infrastructure.
./deploy-idsvr-aws-eks.sh --install./deploy-idsvr-aws-eks.sh --delete
As part of the installation the script will create a new EKS cluster as per the configuration options defined in infrastructure-config/infra-config.json.
Please ensure that the correct AWS region is configured in the infrastructure-config/infra-config.json file.
Installation Prerequisites
The following prerequisites must be met before proceeding ahead with the installation.
Please also copy a license file to the idsvr-config/license.json location. If needed, you can also get a free community edition license from the Curity Developer Portal.
Deployment
First clone the installation repository to your local computer
git clone git@github.com:curityio/curity-idsvr-aws-eks-demo-installation.gitcd curity-idsvr-aws-eks-demo-installation
Run the installation
./deploy-idsvr-aws-eks.sh --install
The installation script prompts for eks cluster creation and deploys all of the needed infrastructure components in AWS along with a customized docker image containing the required phantom-token plugin for the NGINX Ingress controller.
Add following entry to the /etc/hosts file after the installation is completed to access the systems. Replace the placeholder text with actual load balancer IP address.
< LoadBalancer-IP > admin.example.eks login.example.eks api.example.eks
Stop the environment
./deploy-idsvr-aws-eks.sh --stop
Start the environment
./deploy-idsvr-aws-eks.sh --start
View logs
kubectl -n curity logs -f -l role=curity-idsvr-adminkubectl -n curity logs -f -l role=curity-idsvr-runtimekubectl -n ingress-nginx logs -f -l app.kubernetes.io/component=controllerkubectl -n api logs -f -l app=example-api
Here are a few useful kubectl commands
kubectl get namespaces # Get all namespaces in the clusterkubectl get nodes -o wide # Get all of the worker nodes in the clusterkubectl get pods -n curity # Get all pods running the curity namespacekubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx # Get all pods running the ingress-nginx namespacekubectl get pods -n api # Get all pods running the api namespacekubectl get ingress -n curity # Get ingress rules defined in the curity namespacekubectl get ingress -n api # Get ingress rules defined in the api namespacekubectl -n ingress-nginx get svc ingress-nginx-controller -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}" # Get public ip address of the load balancer
Later, when you have finished with this tutorial, run the following command to free cloud resources
./deploy-idsvr-aws-eks.sh --delete
Trust Self-signed Root CA Certificate
All of the URLs are accessible over https for secure communication. In the demo setup, self-signed certificates are used, but since they are not trusted by default by the browser, you must add the root CA certificate to the operating system's truststore to prevent untrusted certificate warnings.
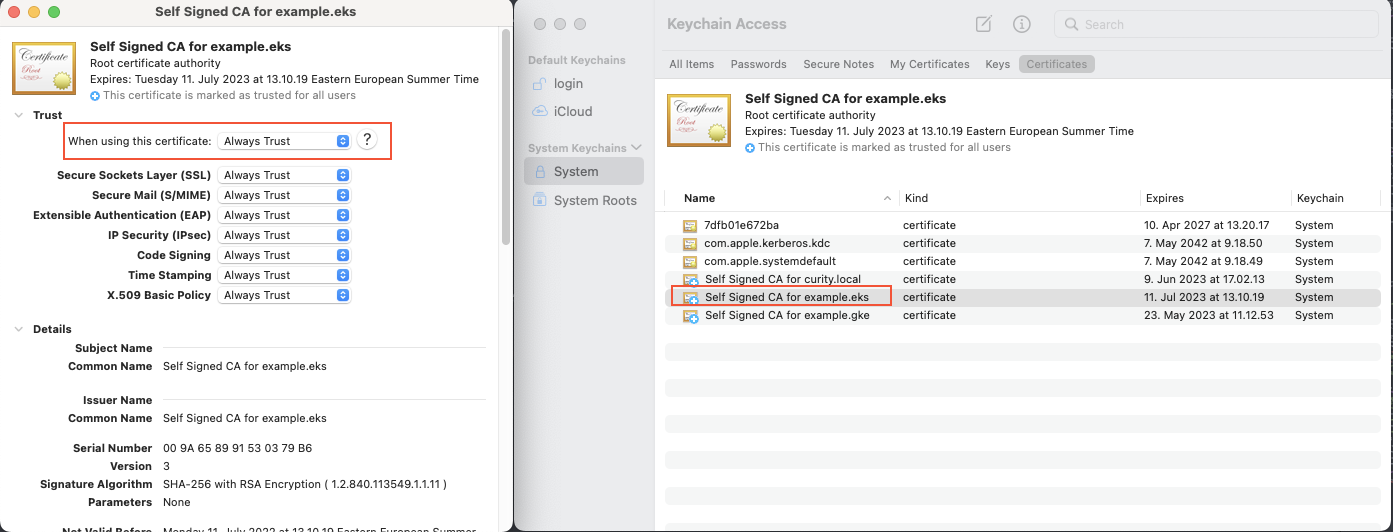
Add the self-signed root CA certificate certs/example.eks.ca.pem to the operating system trust store.
| Operating System | Location |
|---|---|
| macOS | Key Chain / System / Certificates |
| Windows | Microsoft Management Console / Certificates / Local Computer / Trusted Root Certification Authorities |
Curity Identity Server Configuration
The idsvr-config/helm-values.yaml.template file contains the Curity Identity Server deployment configuration. You can add any additional configurations to the file if needed.
An exhaustive set of configuration options can be found in the GitHub repository.
NGINX Ingress Controller Configuration
NGINX Ingress controller configuration in this example has been updated to add the support for phantom token plugin which runs on calling the example API endpoint. For more details about usage and configuration of plugins in Ingress controllers in the Kubernetes environment, please refer to Integrating Plugins with Kubernetes article.
Testing
Run the following steps to test the phantom token flow. These steps will be same irrespective of the type of Ingress controller deployed :
1. Obtain an opaque access token (a.k.a reference token) using client credentials grant type
curl --location --request POST 'https://login.example.eks/oauth/v2/oauth-token' \--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \--data-urlencode 'client_id=example-api' \--data-urlencode 'client_secret=Password123' \--data-urlencode 'scope=read' \--data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials'
The response returned to the client includes an opaque access token.
{"access_token":"_0XBPWQQ_453276d1-8c29-4913-be07-e1f16b0323e3","scope":"read","token_type":"bearer","expires_in":299}
2. Call the API proxy endpoint using the opaque access token
curl https://api.example.eks/echo -H 'Authorization: Bearer _0XBPWQQ_453276d1-8c29-4913-be07-e1f16b0323e3' | jq .
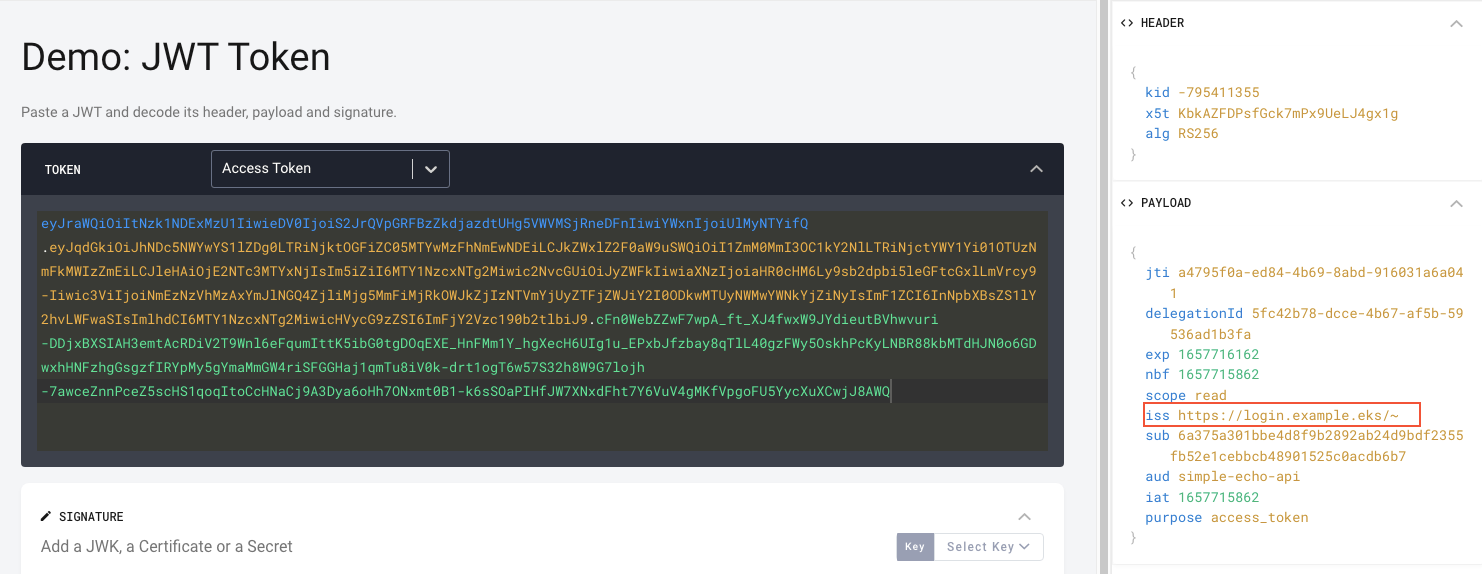
3. Observe that the opaque access token was transformed in to a by-value access token, that is into a JWT by the phantom token plugin and passed to the upstream example-api call. The API logs the token and also returns it as response for easy verification.
kubectl -n api logs -f -l app=example-apiExample API listening on port : 3000JWT token echoed back from the upstream API = eyJraWQiOiIxMjEyNzc5MTk1IiwieDV0IjoiN25LNEFDeDA3VHVWd0Q1d0pvejByYmR2YVhFIiwiYWxnIjoiUlMyNTYifQ.eyJqdGkiOiJjNGNjZTJkYy1hODdiLTQwMmEtOWY2Ny01ZTBmZDlhMmQ1ZjgiLCJkZWxlZ2F0aW9uSWQiOiI1OTYxYzI5ZS0zOWE1LTQ3NTItODVlNC1kODE1OGZlZTg2N2QiLCJleHAiOjE2NTIzMzQ4NDYsIm5iZiI6MTY1MjMzNDU0Niwic2NvcGUiOiJyZWFkIiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9sb2dpbi5leGFtcGxlLmdrZS9-Iiwic3ViIjoiNmEzNzVhMzAxYmJlNGQ4ZjliMjg5MmFiMjRkOWJkZjIzNTVmYjUyZTFjZWJiY2I0ODkwMTUyNWMwYWNkYjZiNyIsImF1ZCI6InNpbXBsZS1lY2hvLWFwaSIsImlhdCI6MTY1MjMzNDU0NiwicHVycG9zZSI6ImFjY2Vzc190b2tlbiJ9.wx2mumnlq_YVTfbxUdJXtwhwAANTkC7avBLhg5G-gi52Sc8veD8PMM3ZwszkE_3ejDAtXpizAI7mWnzMy45cHMTviJUbxjJf7-xsi3izKE8d-tmECfEJGRwCXmlG0kguwKwC1IStExU6-KBGQ1sfftkDBbp3mYsFDTGYxumtm0wInBf0_tuKP1m625h_Xs-S-4pBBRa7BvDGCq7bNzE8kbnRELQXXJxExEgMIeLtvaCg5nK5KYMfA20Ah-X65tkX4XbXZnrd8IkQK0nwsNMC0jzauw66PmsvHB2jEvR-QmQBx7D_Pgme62nqcvMDzPavzzsj5Pi4PGJ75XpFa9ptGw
Decode and study the JWT, you can use OAuth Tools to decode JWT tokens and run various OAuth flows.
eyJraWQiOiItNzk1NDExMzU1IiwieDV0IjoiS2JrQVpGRFBzZkdjazdtUHg5VWVMSjRneDFnIiwiYWxnIjoiUlMyNTYifQ.eyJqdGkiOiJhNDc5NWYwYS1lZDg0LTRiNjktOGFiZC05MTYwMzFhNmEwNDEiLCJkZWxlZ2F0aW9uSWQiOiI1ZmM0MmI3OC1kY2NlLTRiNjctYWY1Yi01OTUzNmFkMWIzZmEiLCJleHAiOjE2NTc3MTYxNjIsIm5iZiI6MTY1NzcxNTg2Miwic2NvcGUiOiJyZWFkIiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9sb2dpbi5leGFtcGxlLmVrcy9-Iiwic3ViIjoiNmEzNzVhMzAxYmJlNGQ4ZjliMjg5MmFiMjRkOWJkZjIzNTVmYjUyZTFjZWJiY2I0ODkwMTUyNWMwYWNkYjZiNyIsImF1ZCI6InNpbXBsZS1lY2hvLWFwaSIsImlhdCI6MTY1NzcxNTg2MiwicHVycG9zZSI6ImFjY2Vzc190b2tlbiJ9.cFn0WebZZwF7wpA_ft_XJ4fwxW9JYdieutBVhwvuri-DDjxBXSIAH3emtAcRDiV2T9Wnl6eFqumIttK5ibG0tgDOqEXE_HnFMm1Y_hgXecH6UIg1u_EPxbJfzbay8qTlL40gzFWy5OskhPcKyLNBR88kbMTdHJN0o6GDwxhHNFzhgGsgzfIRYpMy5gYmaMmGW4riSFGGHaj1qmTu8iV0k-drt1ogT6w57S32h8W9G7lojh-7awceZnnPceZ5scHS1qoqItoCcHNaCj9A3Dya6oHh7ONxmt0B1-k6sSOaPIHfJW7XNxdFht7Y6VuV4gMKfVpgoFU5YycXuXCwjJ8AWQ
Summary
You have learned how to deploy the Curity Identity Server and manage custom plugins with the NGINX Ingress Controller in the AWS Elastic Kubernetes Engine and tested the workings of the phantom token flow. For further information, please refer to the Phantom Token Flow.

Join our Newsletter
Get the latest on identity management, API Security and authentication straight to your inbox.

Start Free Trial
Try the Curity Identity Server for Free. Get up and running in 10 minutes.
Start Free TrialWas this helpful?




