On this page
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) Authorization draft specification enables an open ecosystem where AI agents securely connect to APIs using OAuth. The Design MCP Authorization for APIs article explains the security considerations when organizations expose sensitive API data to AI agents using MCP. This page and the related GitHub repository supplement the design article with a practical example.
This tutorial first explains how to run the deployment example from the GitHub repository on your local computer. The deployment includes an MCP server as a secured entry point to APIs, so that AI agents can use MCP clients to connect, with zero-delay onboarding. The MCP technical flow section then highlights particular implementation details.
Example Overview
The code example exposes an API that provides secured information on stock prices to AI agents. Security controls restrict who can access the data. In the example, an AI agent would only have read permissions to the user's authorized stock data. The overall deployment uses a number of components, where all backend components run behind an API gateway. In the example, the MCP server is a stateless utility API uses the Streamable HTTP Transport to provide an API entry point.

The Curity Identity Server acts as an OAuth authorization server to enable a number of security behaviors.
- The MCP client runs OAuth flows that use security standards.
- The MCP client receives a locked-down opaque access token.
- The MCP client calls the MCP server with the opaque access token.
- The Phantom Token Plugin introspects the opaque access token and sends a JWT access token to the MCP server.
- The MCP server validates the JWT access token and checks for its required audience.
- The MCP server tool uses token exchange to change the audience of the access token.
- The MCP server tool sends a JWT access token to upstream APIs.
- The upstream API implements the main authorization to control access to business resourcs.
Deploy Backend Components
The example deployment provides the following backend endpoints.
| Endpoint | URL | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Stocks API | https://api.demo.example/stocks | The API entry point for non MCP clients. |
| MCP Server Entry Point | https://mcp.demo.example | Endpoint that the MCP client integrates with. |
| MCP Resource Server Metadata URL | https://mcp.demo.example/.well-known/oauth-protected-resource | Used by the MCP client to discover the MCP server's authorization server. |
| Curity Identity Server OAuth Metadata URL | https://login.demo.example/.well-known/oauth-authorization-server | The authorization server metadata endpoint of the Curity Identity Server. |
| Curity Identity Server Admin UI | https://admin.demo.example/admin | The administration user interface for the Curity Identity Server. |
| Test Email Inbox | https://mail.demo.example | A mail server for testing purposes that lets you receive emails for test users. |
Clone the GitHub link at the top of this page to a local folder and run a command shell in that folder. Ensure that your local computer meets the prerequisites from the repository's README file. Then run the following commands to deploy all backend components, where LICENSE_FILE_PATH points to your license file for the Curity Identity Server. If you do not have any license for the Curity Identity Server yet, download a trial license from Curity's Developer Portal.
export LICENSE_FILE_PATH=~/Desktop/license.json./build.sh./deploy.sh
Then follow the README instructions to add hostnames to the /etc/hosts file and configure operating system trust for the development SSL certificate. You will then be able to resolve the example URLs on your local computer.
Run MCP Clients
AI agents should use an MCP client that implements the client side of the MCP draft authorization specification. In an open ecosystem of AI agents you typically do not control the MCP client's OAuth code and rely upon standards-based integrations. To demonstrate the flows, the GitHub repository includes a variety of free clients, which use the interoperable security standards from the MCP authorization protocol to connect to the deployed environment. The GitHub repository explains the setup instructions for each client. You can follow a similar approach to integrate other clients, such as a paid version of ChatGPT.
MCP Authorization Technical Flow
Running an MCP client triggers an initial request to https://mcp.demo.example which triggers the standards-based flow from the MCP authorization draft specification. The following sections explain some key points about the example deployment and the security techniques it uses.
API Gateway Routes
The example deployment uses the Kong API gateway to expose endpoints. The routes use host names and paths from client requests to invoke APIs. In the API gateway configuration, the MCP server uses the Kong Phantom Token Plugin and requires a valid opaque access token.
services:- name: mcp-serverurl: http://utility-mcp-server:3000/routes:- name: mcp-server-routehosts:- mcp.demo.examplepaths:- /plugins:- name: phantom-tokenconfig:introspection_endpoint: http://idsvr:8443/oauth/v2/oauth-introspectclient_id: api-gateway-clientclient_secret: Password1token_cache_seconds: 900
Discovery
When an MCP client first connects to the MCP server it does not have a valid access token. According to the MCP authorization draft specification, the backend should send an HTTP 401 response with a WWW-Authenticate response header that provides an OAuth protected resource metadata endpoint and scopes for the MCP server that the client calls. The phantom token plugin implements this response.
HTTP/1.1 401 UnauthorizedWWW-Authenticate: Bearer error='"invalid_token", resource_metadata="https://mcp.demo.example/.well-known/oauth-protected-resource" scope="stocks/read"
The MCP client then calls the MCP server's resource metadata URL, which returns details about supported scopes and the authorization server that the MCP server uses.
{"resource": "https://mcp.demo.example/","resource_name": "MCP Server","scopes_supported": ["stocks/read"],"authorization_servers": ["https://login.demo.example"]}
Next, the MCP client takes the authorization_servers value and appends ./well-known/oauth-authorization-server to it, to form the OAuth authorization server metadata URL. The MCP client calls this URL and receives data from the Curity Identity Server, which includes details about its OAuth capabilities like OAuth endpoints and supported client authentication.
{"acr_values_supported": ["urn:se:curity:authentication:email:email"],"authorization_endpoint": "https://login.demo.example/oauth/v2/oauth-authorize","authorization_response_iss_parameter_supported": true,"authorization_signing_alg_values_supported": ["PS256"],"claims_parameter_supported": true,"code_challenge_methods_supported": ["S256","plain"],"grant_types_supported": ["refresh_token","implicit","client_credentials","password","https://curity.se/grant/accesstoken","authorization_code"],"introspection_endpoint": "https://login.demo.example/oauth/v2/oauth-introspect","introspection_endpoint_auth_methods_supported": ["client_secret_post","client_secret_basic"],"issuer": "https://login.demo.example/oauth/v2/oauth-anonymous","jwks_uri": "https://login.demo.example/oauth/v2/oauth-anonymous/jwks","pushed_authorization_request_endpoint": "https://login.demo.example/oauth/v2/oauth-authorize/par","registration_endpoint": "https://login.demo.example/token-service/oauth-registration","registration_endpoint_auth_methods_supported": ["Bearer"],"registration_endpoint_auth_signing_alg_values_supported": [],"response_modes_supported": ["fragment","fragment.jwt","jwt","form_post","query","query.jwt","form_post.jwt"],"response_types_supported": ["code","code id_token",],"scopes_supported": ["address","phone","email","openid","profile","stocks/read"],"token_endpoint": "https://login.demo.example/oauth/v2/oauth-token","token_endpoint_auth_methods_supported": ["client_secret_post","client_secret_basic"]}
Dynamic Client Registration
The client can use the MCP Scope Selection Strategy and create a DCR request payload with the scopes it needs. The client makes an HTTP POST request to the Curity Identity Server's registration endpoint. To do so, the MCP client uses the registration_endpoint from authorization server metadata and sends a request similar to the following.
{"client_name": "MCP Inspector","grant_types": ["authorization_code"],"redirect_uris": ["http://localhost:6274/callback"],"response_types": ["code"],"scope": "stocks/read","token_endpoint_auth_method": "client_secret_post"}
The Curity Identity Server supports JavaScript Pre-processing Procedures to enforce policies upon registering a dynamic client. In the example, the Curity Identity Server applies a policy for dynamic clients that use the stocks/read scope. The example policy first enforces PKCE, sets the access token lifetime to 15 minutes, disables the use of refresh tokens and sets the client's access token audience(s). The custom property for client_type marks the dynamic client as an MCP client. The client_assurance_level represents the trust level of the MCP client. The name property is used to customize login screens and the template_area property enables the client to use its own customized consent screen.
function result(context) {var request = context.getRequest();var httpMethod = request.getMethod();var attributes = {};if (httpMethod === 'POST') {var body = request.getParsedBodyAsJson();if (body && body.scope) {if (body.scope.split(' ').indexOf('stocks/read') !== -1) {attributes.require_proof_key = true;attributes.access_token_ttl = 900;attributes.refresh_token_ttl = 0;attributes.audiences = ["https://mcp.demo.example/"];attributes.client_type = 'mcp';attributes.client_assurance_level = 1;attributes.name = body.client_name;attributes.template_area = 'mcp-client';}}}return attributes;}
You can view DCR-related settings in the Admin UI. To do so, browse to https://admin.demo.example/admin and use the login credentials from the GitHub repository's README file. Navigate to Token Service → General → Dynamic Registration to see the registered scopes for DCR. Navigate to Token Service → Endpoints → token-service-dynamic-client-registration → Pre-processing Procedure to view the script details.
After it applies the DCR policy, the Curity Identity Server creates a dynamic client, assigns it a generated client ID and client secret and returns it to the MCP client, which should persist the details and use them for subsequent connections to the Curity Identity Server.
{"access_token_ttl": 900,"audiences": ["https://mcp.demo.example/"],"client_id": "15d64f90-5df1-4ab8-ae48-af0aa2e6d562","client_id_issued_at": 1759825565,"client_name": "MCP Inspector","client_secret": "lYo5fRR4mMn9bTxIbigv9ZCn1lT6BEKuHA3zZpOxR0s","client_secret_expires_at": 0,"default_acr_values": ["urn:se:curity:authentication:email:email"],"grant_types": ["authorization_code"],"post_logout_redirect_uris": [],"redirect_uris": ["http://localhost:6274/callback"],"require_proof_key": true,"requires_consent": true,"response_types": ["code"],"scope": "stocks/read","subject_type": "public","token_endpoint_auth_method": "client_secret_post","token_endpoint_auth_methods": ["client_secret_basic","client_secret_post"]}
User Authentication
User authentication uses an OAuth 2.1 code flow with parameters of the following form (with URL encoding removed for readability). The MCP client sends a resource parameter to instruct the authorization server where it wants to use its access token.
GET /oauth/v2/oauth-authorize?client_id=15d64f90-5df1-4ab8-ae48-af0aa2e6d562&response_type=code&redirect_uri=http://localhost:65343/callback&scope=stocks/read&code_challenge=UDCiyI7N7vjI9vfz0w7m4exLFfHB4-clsyCgnTjh7EA&code_challenge_method=S256&resource=https://mcp.demo.example/Host: login.demo.example
Each user's instance of the MCP client receives a distinct client ID and client secret. User authentication is only allowed for administrator approved users (those included in the backend deployment). Users prove ownership of their corporate email and authenticate with a one-time password.
Console or desktop MCP clients may abruptly trigger user authentication in a disconnected browser window. The example deployment adds a custom HTML label to the email authentication screen to improve the user experience. A customized enter-username.vm template file uses the client's name property that the DCR policy stored against the dynamic client.
<p>${_requestingOAuthClient.properties.name} #message("authenticator.email.enter-username.view.requesting")</p>
The user can then clearly sees which client requests user authentication.

When the browser requests an email address, enter one of the email addresses from the repository's README file. Then, navigate to the test email inbox at https://mail.demo.example, get the one-time password and paste it into the browser window.
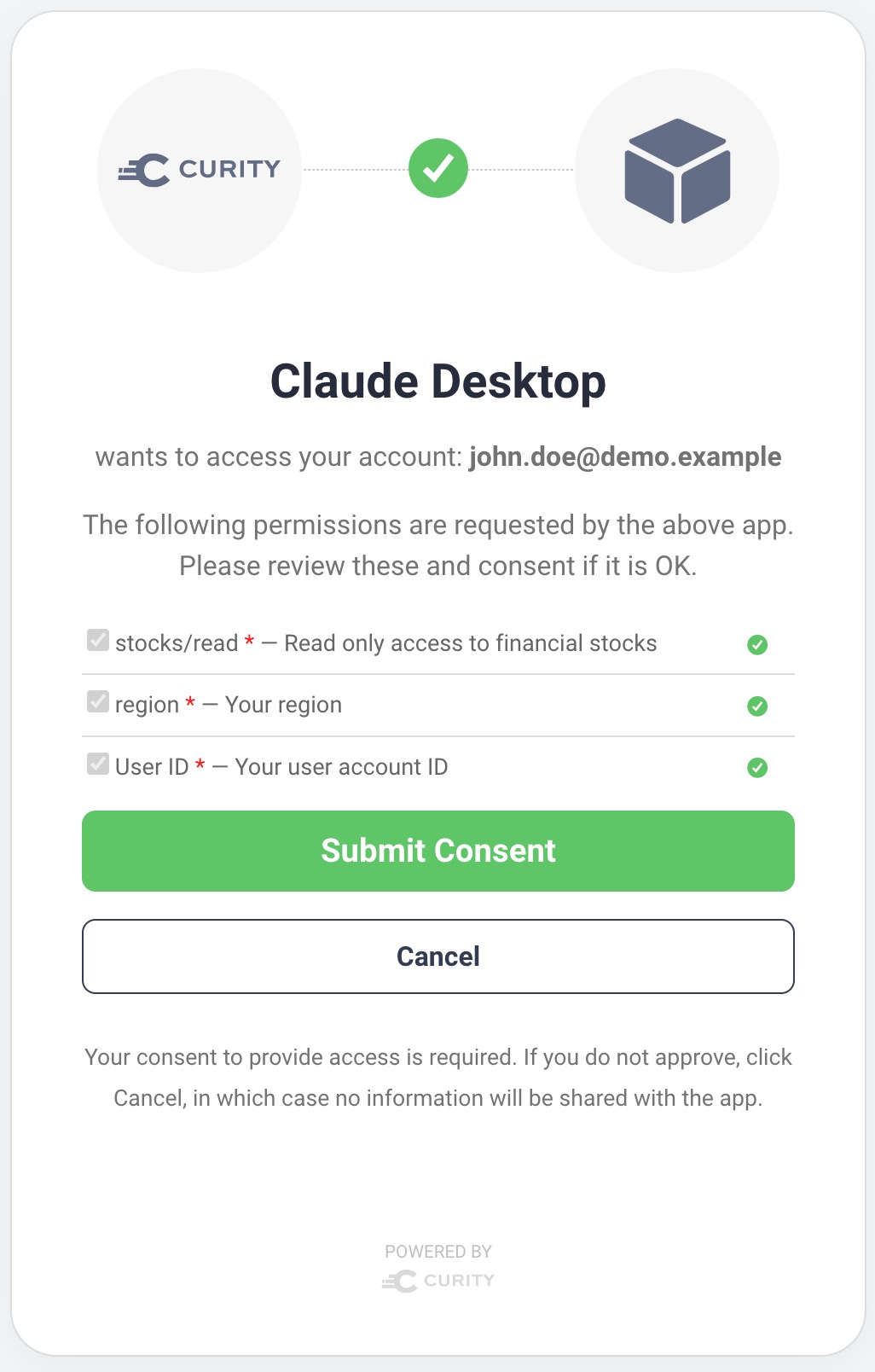
User Consent
The example stocks/read scope contains the following custom claims, in addition to the built-in subject claim issued in OAuth user-level flows:
regionclient_typeclient_assurance_level
The example deployment Customizes the User Consent Form to present an understandable consent experience to the user. The user grants the AI agent permissions to read authorized stock data from the user's region. To avoid user confusion, the consent form hides the client_type and client_assurance_level claims.
After user authentication and consent, the MCP client receives an authorization code and the Curity Identity Server also returns an iss parameter. MCP clients should validate the iss value to help protect against authorization server mix-up attacks, as explained in the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Server Issuer Identification specification from RFC 9207.
Token Issuance
Finally, the MCP client uses its dynamic client ID and client secret and redeems the authorization code for OAuth tokens with a request of the following form.
POST /oauth/v2/token HTTP/1.1Host: login.demo.exampleContent-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedclient_id=15d64f90-5df1-4ab8-ae48-af0aa2e6d562&client_secret=lYo5fRR4mMn9bTxIbigv9ZCn1lT6BEKuHA3zZpOxR0s&grant_type=authorization_code&redirect_uri=http://localhost:65343/callback&code=nqb2raZqZpX44uQ74CJnXwIDnXaYb6Xm&code_verifier=WccahGqMpe4vJ.UIc.jJ7ZpGk6Ex2ig20GkJd2oMK&resource=https://mcp.demo.example/
The MCP client receives a token response that includes a short-lived opaque access token with a limited scope.
{"access_token": "_0XBPWQQ_2fb1bc61-0e98-413c-a44d-d8a46d3bd2f2","expires_in": 900,"scope": "stocks/read","token_type": "bearer"}
Using MCP Tools
Once the example MCP client has a valid opaque access token, it can interact with the secured MCP server's endpoints. On all requests, the MCP client includes the opaque access token in the HTTP Authorization header. The MCP client first requests a list of authorized tools. The MCP client can then invoke those tools on behalf of the user.
The example deployment supports multiple MCP clients. To learn about tool requests you can run the MCP Inspector, which can run MCP client and invoke MCP operations manually, to visualize each step's inputs and outputs:

In a real MCP host, like Claude Desktop, the user instead asks a natural language question and the AI agent can autonomously try to run any tool that the MCP server makes available to the client.

Developing MCP Servers
The code example implements a minimal, stateless MCP server with the TypeScript SDK, to provide API entry points for the MCP client.
const serverInfo = {name: 'utility-mcp-server',version: '1.0.0'};this.mcpServer = new McpServer(serverInfo);this.mcpServer.tool('fetch-stock-prices','A tool to fetch secured information about financial stock prices',this.fetchStockPricesFromApi,);
The MCP server implements JWT access token validation, as for any other resource server. In particular, the MCP server only accepts access tokens whose audience restrictions include the MCP server's identity.
public async validateAccessToken(request: Request, response: Response, next: NextFunction): Promise<void> {{const accessToken = this.readAccessToken(request);if (!accessToken) {throw new ApiError(401, 'invalid_token', 'Missing, invalid or expired access token');}const options = {issuer: this.configuration.requiredIssuer,audience: this.configuration.requiredAudience,algorithms: [this.configuration.requiredJwtAlgorithm],} as JWTVerifyOptions;response.locals.claimsPrincipal = new ClaimsPrincipal(result.payload);next();}
The main role of the MCP server is to call upstream APIs with a JWT access token and return responses to the MCP client. Before doing so, the MCP server uses OAuth token exchange to change the audience of the access token to that of the upstream API.
POST /oauth/v2/oauth-token HTTP/1.1Host: login.example.comContent-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedgrant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:token-exchange&client_id=mcp-server&client_secret=Password1&subject_token=eyJraWQiOiItMTcyNTQxNzE2NyIsIng...&subject_token_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type:access_token&audience=https://api.demo.example
The following code demonstrates the MCP server tool's logic when it calls the upstream API.
private async fetchStockPricesFromApi(extra: RequestHandlerExtra<ServerRequest, ServerNotification>): Promise<CallToolResult> {try {const receivedAccessToken = extra.authInfo?.token || '';const oauthClient = new TokenExchangeClient(this.configuration, this.errorHandler);const exchangedAccessToken = await oauthClient.exchangeAccessToken(receivedAccessToken);const apiClient = new StocksApiClient(this.configuration, this.errorHandler);const data = await apiClient.getStocks(exchangedAccessToken);console.log('MCP server successfully called stocks API');return {content: [{type: "text",text: data}]};} catch (e: any) {return this.toolErrorResponse(e as McpServerError);}}
The example MCP server also returns useful error responses to MCP clients, including WWW-Authenticate headers that comply with the MCP authorization protocol.
API Authorization with Context
The stocks API is where the main business authorization takes place. The stocks API receives access tokens with a JSON payload of the following form and can use claims to enforce its business rules. The example authorization uses the region claim to filter allowed stocks to those for the user's region.
{"jti": "31b921b8-b166-4173-b633-7480bab89456","delegationId": "d94e9d67-b426-4cff-8613-f7cf2b1ca154","exp": 1762337303,"nbf": 1762336403,"scope": "stocks/read","iss": "https://login.demo.example/oauth/v2/oauth-anonymous","sub": "john.doe@demo.example","aud": "https://api.demo.example","iat": 1762336403,"purpose": "access_token","client_assurance_level": 1,"client_type": "mcp","region": "USA"}
The API also receives the client_type and client_assurance_level claims as runtime information about the MCP client. The API can easily use those claims to return an HTTP 403 forbidden response for operations that it does not want AI agents to call. The API could use the client_assurance_level claim to only allow access to clients that authenticate with a strong identity. For example, those endpoints could be limited to backend components that use workload identities.
Developing MCP Clients
To develop a custom MCP client in addition to MCP servers, you could base an approach on the simpleOAuthClient.ts module from the TypeScript SDK example client, so that the underlying SDK does most of the work.
Consider any particular requirements of MCP hosts that will run your MCP client. Many MCP hosts, like Claude, support a generic mechanism, where you configure a command and a set of arguments to connect to MCP servers. MCP hosts often provide a default MCP client implementation with a local proxy like mcp-remote, where users add a connection with the MCP server's URL, resulting in settings similar to those shown below.
{"mcpServers": {"curity-demo": {"command": "npx","args": ["mcp-remote", "https://mcp.demo.example"],}}}
Conclusion
This tutorial explained some key points of the MCP deployment example, so that you can connect an MCP client to an MCP server and operate with least-privilege API access. The Curity Identity Server gives you control over the deeper security behaviors, so that your APIs can restrict the level of access granted to AI components.
An OAuth architecure provides you with the building blocks to securely connect to APIs from any type of client. With the right separation it should be straightforward to add AI agents as a new type of API client. Done correctly, you should only need to implement a lightweight MCP server to provide a new entry point to APIs.

Join our Newsletter
Get the latest on identity management, API Security and authentication straight to your inbox.

Start Free Trial
Try the Curity Identity Server for Free. Get up and running in 10 minutes.
Start Free TrialWas this helpful?






